Description
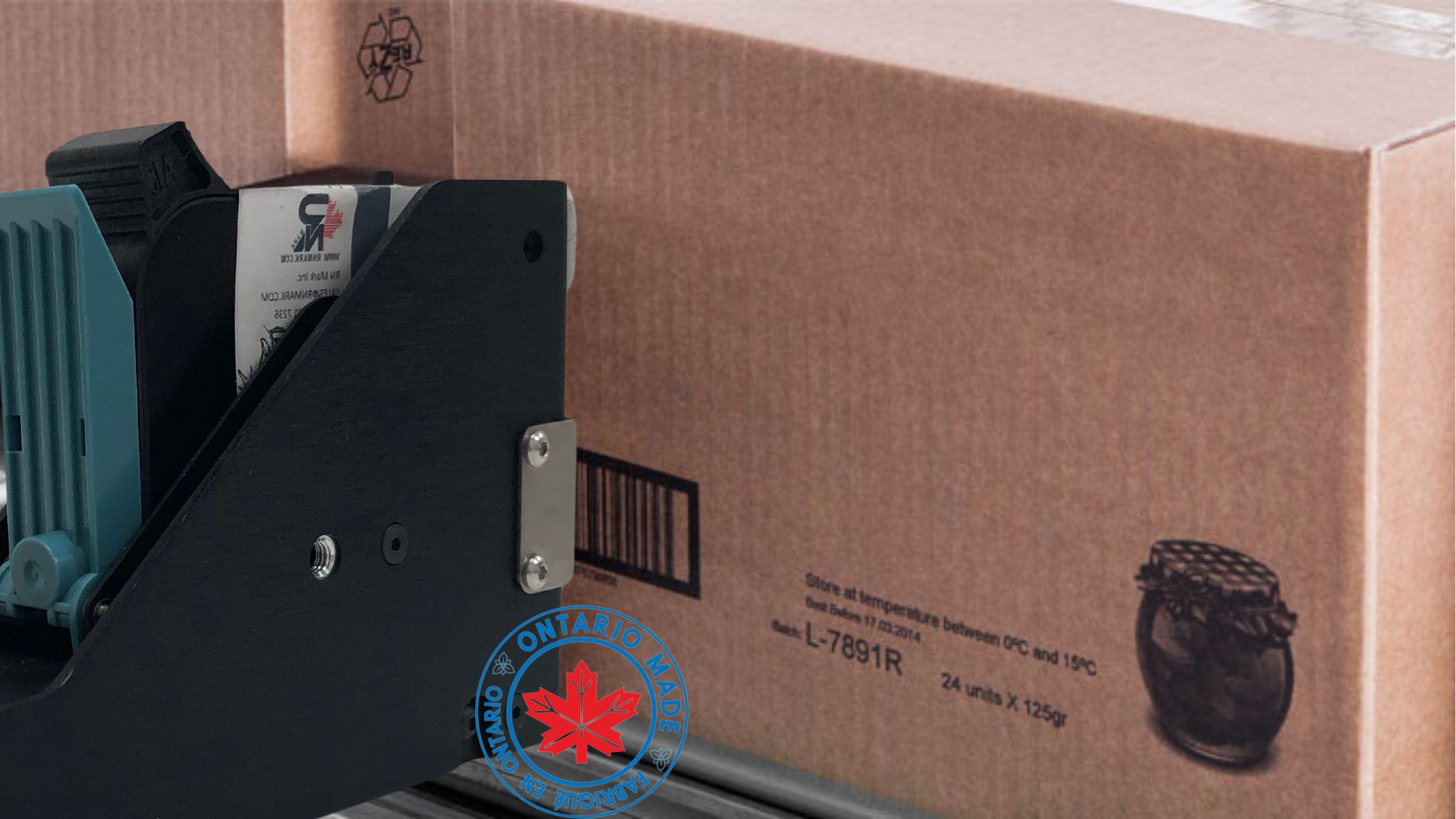
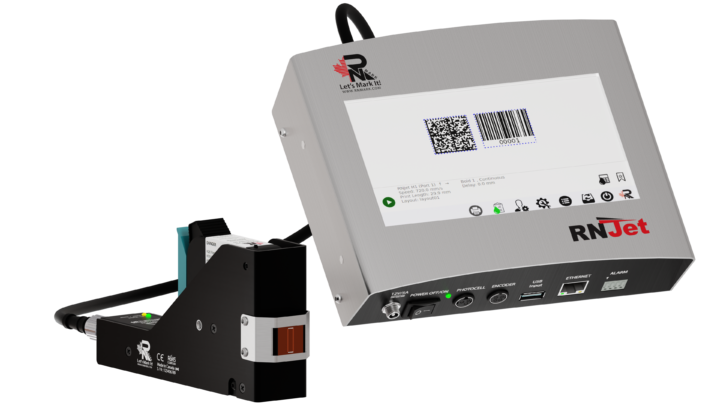
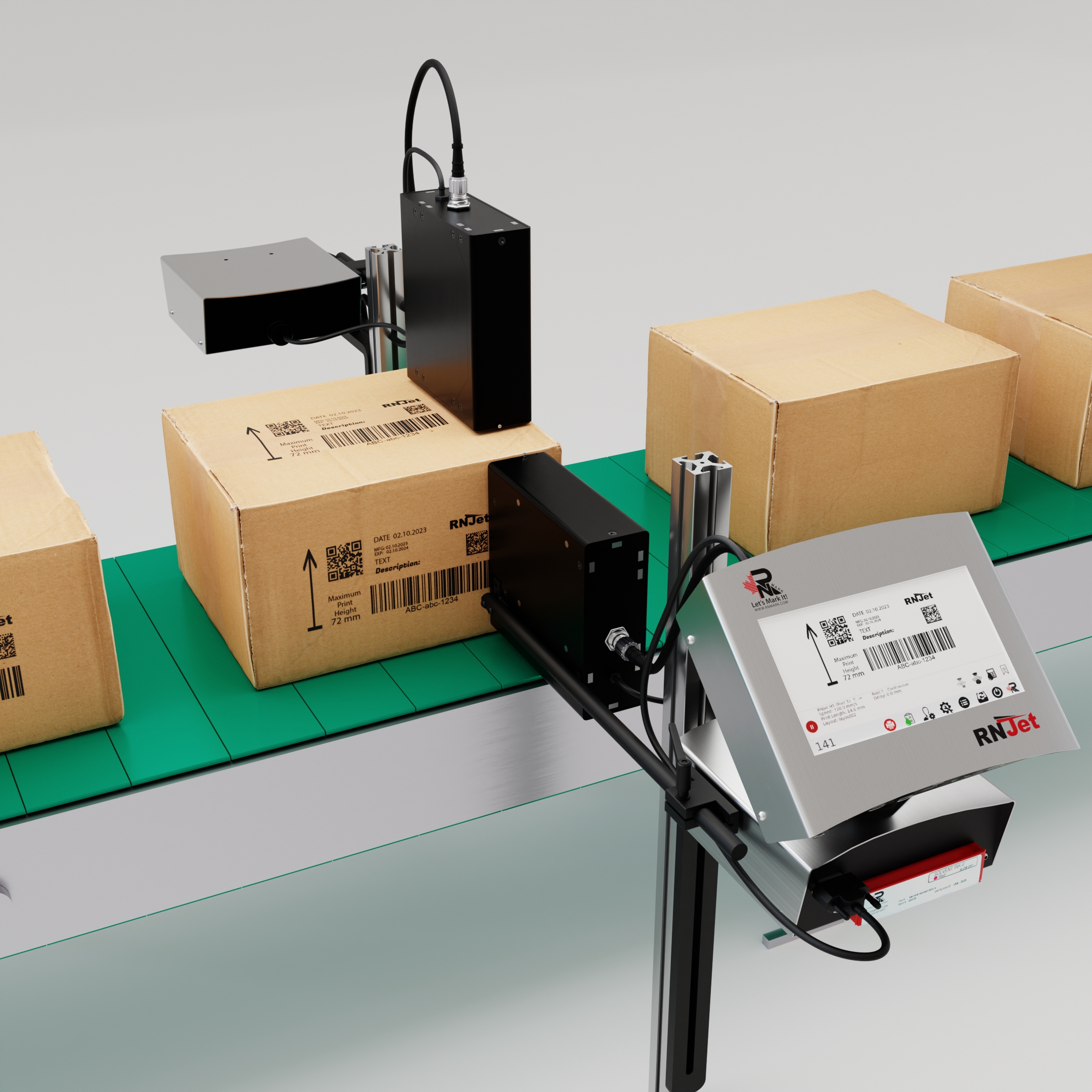
The best option is to mark your products with NO maintenance, easy to operate date coder machine from a Canadian Manufacturer. Ideal for small production with no mess and highly economical!
Which application you could mark with date coder printer RNJet H1+:
- Automotive
- Brewery Beer Cans
- Egg Printing
- Face Respirators, PPE & MASKS
- Hand Sanitizer Bottles
- Pallets and Wood Products
- Food & Condiments
- Pharmaceutical & Medical
- Cardboard & Carton
- Pet Food
- Grain & Cement
- Beverage
- Electronic Components
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Dairy
Date Coding with RNJet H1+:
- LOT Number
- EXP and MFG Dates (auto)
- Logo
- Barcode (any type, including QR-Code)
- Shift Code (auto)
- Data-base
- Counter
- UDI (GS1 Data Matrix etc.)
- Ingredients
For more information do not hesitate to contact us or visit the related product page.
Date Coders and Date Coding Machines
What is Date Coding?
Date coding is the process of applying a date, expiration date, or other time-sensitive information to products, packaging, or other materials. This helps track the freshness, shelf life, and production timeline of goods. Date coding is commonly used in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
Date Coding Machines
Date coding machines are specialized equipment used to print, stamp, or emboss date information onto products or packaging. These machines come in a variety of types, including:
- Inkjet Coders: Use inkjet technology to print date codes, lot numbers, and other variable information directly onto products or packaging.
- Thermal Transfer Coders: Use heat-activated ribbons to transfer date and other codes onto labels or packaging materials.
- Laser Coders: Employ laser technology to etch date and identification codes onto product surfaces.
- Continuous Ink Jet (CIJ) Coders: Spray tiny ink droplets to create date, batch, and other codes on products.
- Mechanical Coding Machines: Use physical stamps or wheels to imprint date and other information.
These machines are designed for high-speed, accurate, and reliable date coding to meet industry regulations and traceability requirements.
The Importance of Date Coding
Date coding plays a crucial role in ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance across many industries. Some key benefits of effective date coding include:
- Freshness and Shelf Life Management: Date codes allow businesses to track product expiration dates and rotate inventory accordingly, minimizing waste and ensuring customers receive fresh goods.
- Traceability and Recall Management: In the event of a product recall, date codes help identify affected batches and streamline the recall process, protecting public health and a company’s reputation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have strict regulations around date coding and labeling to provide transparency for consumers and ensure product safety. Proper date coding helps businesses meet these legal requirements.
- Inventory Control: Date codes enable businesses to better manage stock levels, prevent overstocking, and ensure products are sold within their optimal timeframe.
- Brand Protection: Consistent, high-quality date coding reinforces a brand’s image of reliability and quality in the eyes of customers.
Types of Date Codes
There are several common date code formats used across industries:
- Expiration Date: Indicates the last day a product should be consumed for peak quality and safety.
- Best Before/Best By Date: Suggests the date by which the product should be consumed for optimal freshness and flavor, though it may still be safe to use after this date.
- Production Date: Specifies the date the product was manufactured.
- Lot or Batch Number: Allows for the identification of a specific production run or batch of products.
- Julian Date: Uses a 3-4 digit code to represent the day of the year (e.g., 123 = May 3rd).
The choice of date code format depends on the product, industry regulations, and the needs of the business and its customers.
Designing Effective Date Coding Systems
Implementing a successful date coding system requires careful planning and consideration of several key factors:
- Coding Technology: Selecting the right date coding machine(s) based on factors like production speed, print quality, and integration with existing packaging lines.
- Code Placement: Determining the optimal location on the product or packaging to ensure date codes are clearly visible and accessible.
- Code Content and Format: Choosing the appropriate date code type and format to meet regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
- Ink and Ribbon Selection: Ensuring the coding media is compatible with the product material and environment to maintain legibility over the product’s shelf life.
- Operator Training: Educating staff on proper machine operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting to minimize coding errors and downtime.
- Data Integration: Integrating date coding systems with enterprise resource planning (ERP) or inventory management software to streamline data tracking and reporting.
By addressing these elements, businesses can develop a robust date coding strategy that enhances product traceability, quality control, and overall operational efficiency.
Emerging Trends in Date Coding
The date coding industry is continuously evolving, with several emerging trends shaping the future of this critical function:
- Increased Automation: Date coding machines are becoming more integrated with packaging lines and enterprise systems, reducing the potential for human error and improving overall efficiency.
- Serialization and Unique Identifiers: Some industries, such as pharmaceuticals, are adopting serialized date codes and unique product identifiers to enhance traceability and combat counterfeiting.
- Sustainable Coding Solutions: Eco-friendly coding technologies, such as water-based inks and laser coding, are gaining traction as businesses seek to reduce their environmental impact.
- Data-Driven Insights: Advanced analytics and machine learning are enabling businesses to leverage date coding data to optimize inventory management, predict demand, and make more informed business decisions.
- Blockchain Integration: The integration of date coding systems with blockchain technology can provide an immutable, transparent record of a product’s journey from manufacturer to consumer, further enhancing traceability.
As these trends continue to evolve, businesses that stay ahead of the curve and adopt innovative date coding strategies will be well-positioned to meet the growing demands of consumers and regulatory bodies.
Conclusion
Date coding is a critical function that ensures product quality, safety, and compliance across a wide range of industries. By understanding the various date coding technologies, best practices, and emerging trends, businesses can develop effective date coding systems that drive operational efficiency, enhance brand reputation, and ultimately better serve their customers.